|
13 | 13 | [](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-ai-agents/actions/workflows/build.yml) |
14 | 14 | [](https://pypi.org/project/jupyter-ai-agents) |
15 | 15 |
|
16 | | -*The Jupyter AI Agents are equipped with tools like 'execute', 'insert_cell', and more, to transform your Jupyter Notebooks into an intelligent, interactive workspace!* |
| 16 | +🪐 ✨ AI Agents for JupyterLab with 🛠️ MCP tools - Chat interface for intelligent notebook interaction, code execution, and workspace management. |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +## 💬 Chat Interface |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +Experience seamless AI-powered assistance directly within JupyterLab through our intuitive chat interface: |
17 | 21 |
|
18 | 22 |  |
19 | 23 |
|
20 | | - |
| 24 | +The chat interface is built using [Pydantic AI](https://github.com/pydantic/pydantic-ai) for robust AI agent orchestration and [Vercel AI Elements](https://github.com/vercel/ai-elements) for the user interface components. |
21 | 25 |
|
22 | | -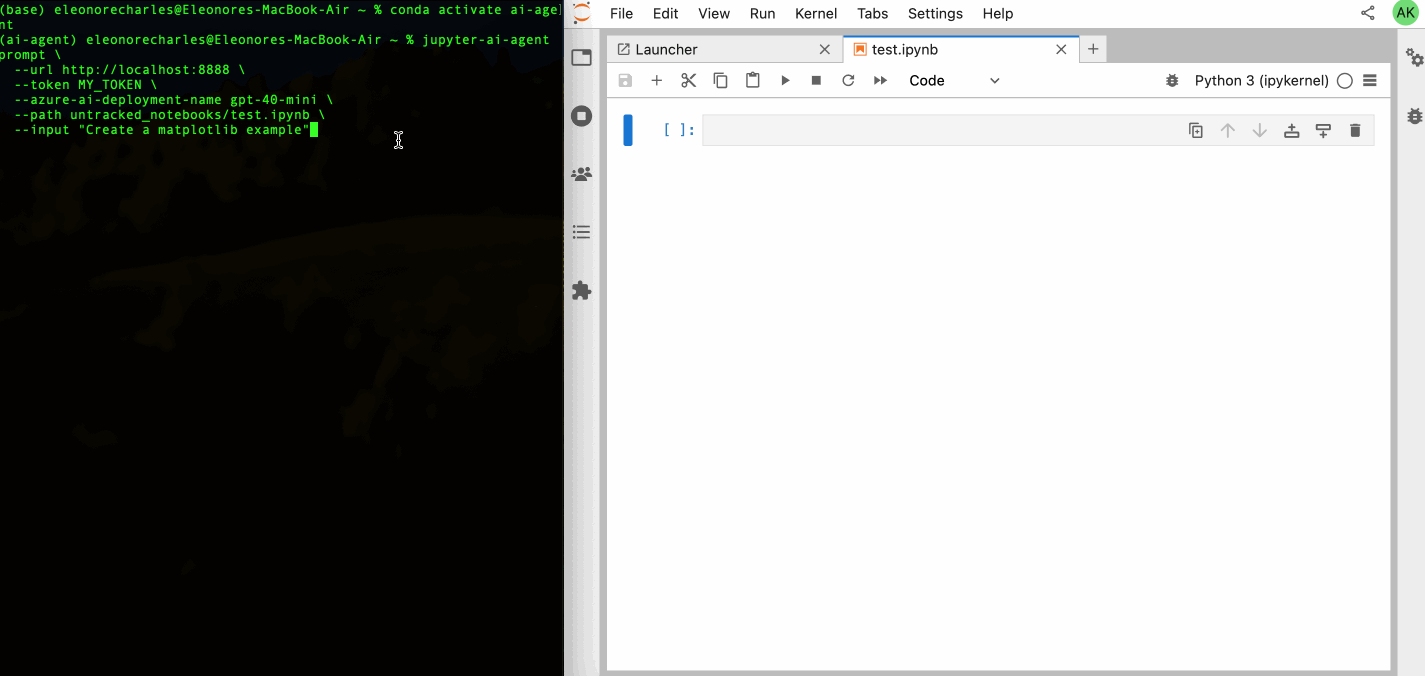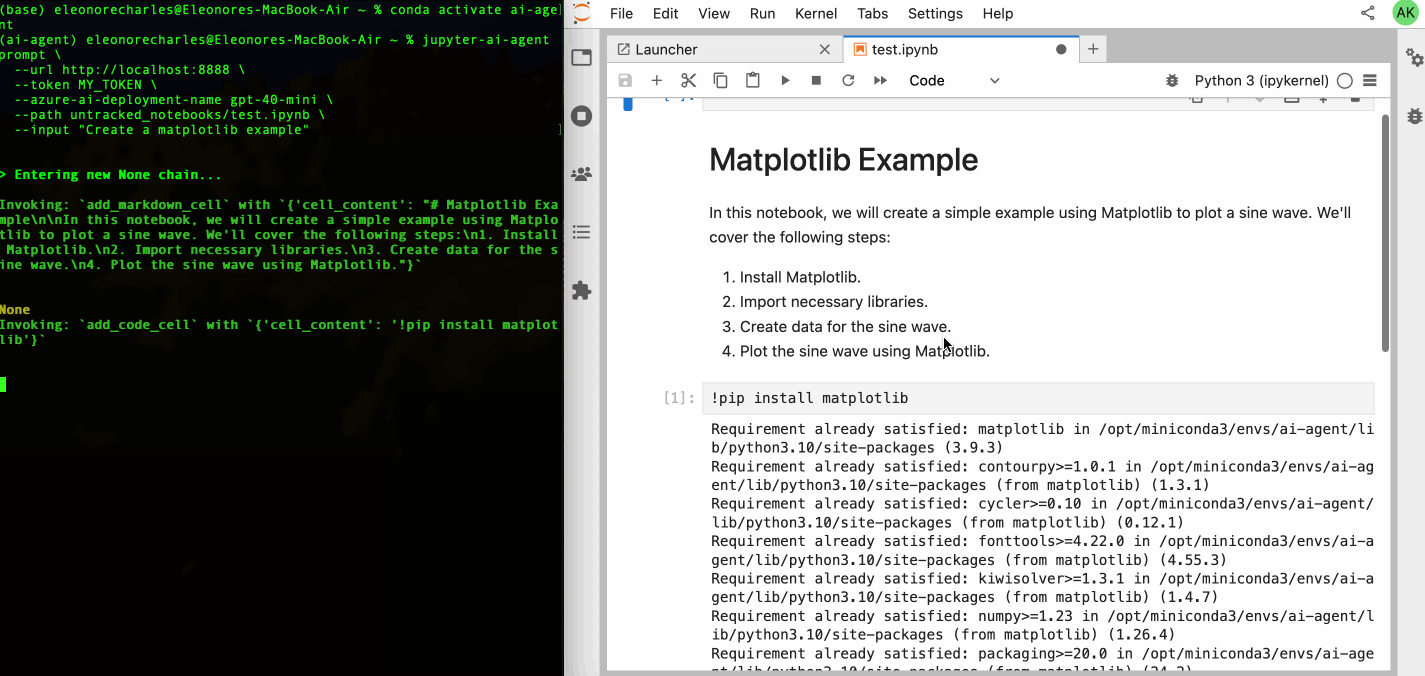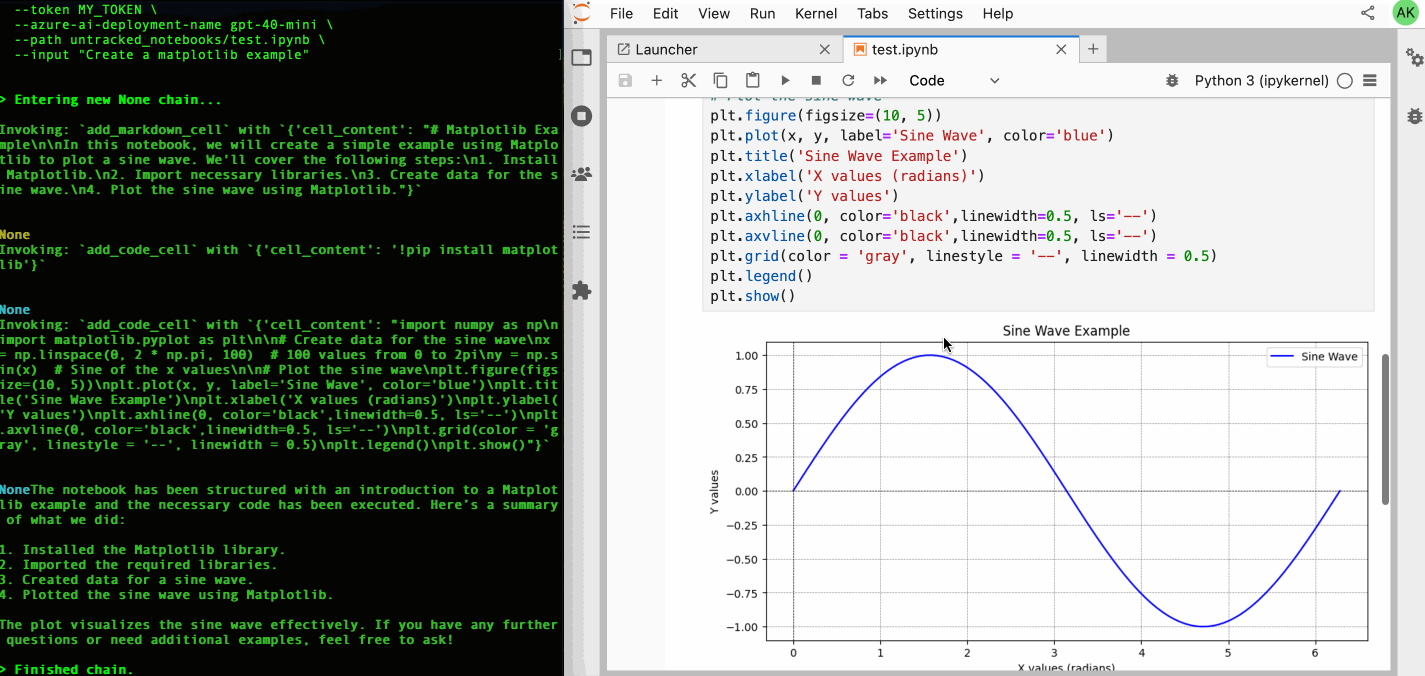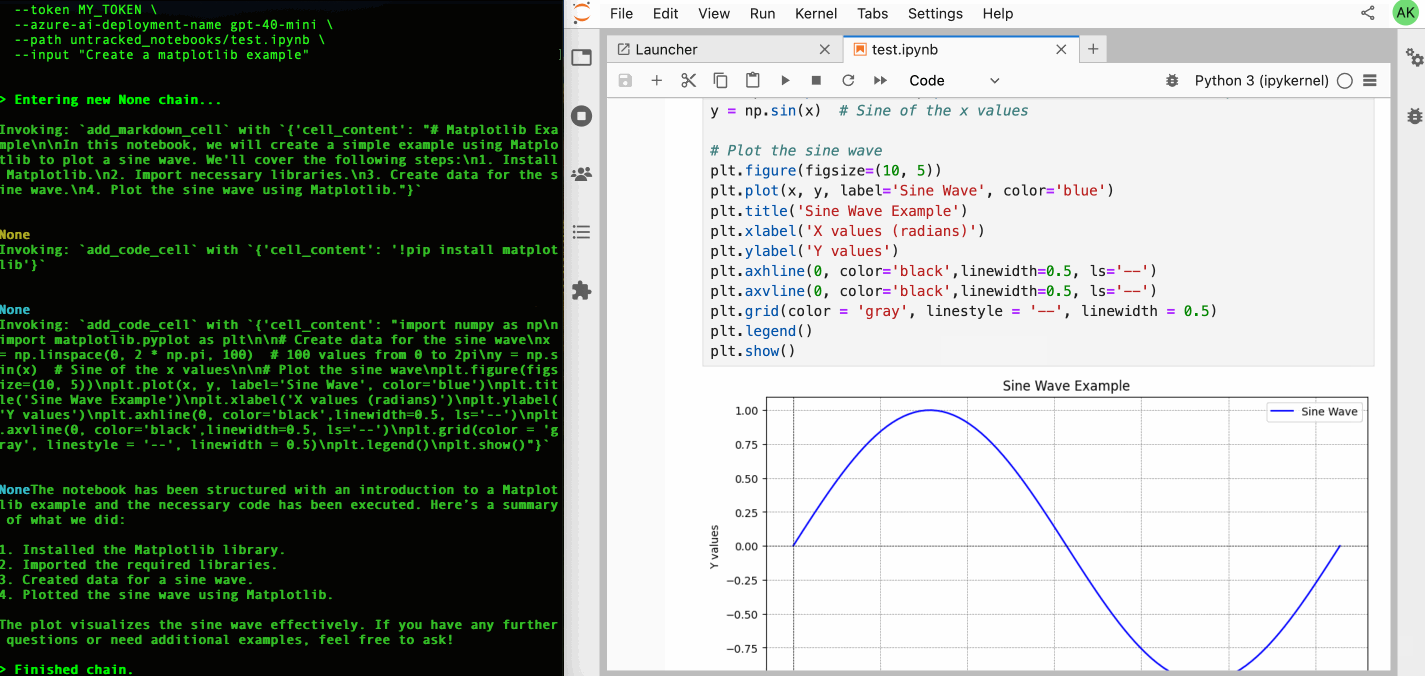 |
| 26 | +### MCP Server Integration |
23 | 27 |
|
24 | | -Jupyter AI Agents empowers **AI** models to **interact** with and **modify Jupyter Notebooks**. The agent is equipped with tools such as adding code cells, inserting markdown cells, executing code, enabling it to modify the notebook comprehensively based on user instructions or by reacting to the Jupyter notebook events. |
| 28 | +By default, the [Jupyter MCP Server](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server) is started as a Jupyter server extension, providing access to all Jupyter MCP server tools directly through the chat interface. This enables the AI agent to interact with notebooks, execute code, manage files, and perform various Jupyter operations seamlessly. |
25 | 29 |
|
26 | | -This Agent is **innovative** as it is designed to **operate on the entire Notebook**, not just at the cell level, enabling more comprehensive and seamless modifications. |
| 30 | + |
27 | 31 |
|
28 | | -The Agent can also run separetely from the Jupyter server as the communication is achieved through RTC via the [Jupyter NbModel Client](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-nbmodel-client) and the [Jupyter Kernel Client](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-kernel-client). |
| 32 | +### Getting Started with Chat |
29 | 33 |
|
30 | | -``` |
31 | | -Jupyter AI Agents <---> JupyterLab |
32 | | - | |
33 | | - | RTC (Real Time Collaboration) |
34 | | - | |
35 | | -Jupyter Clients |
36 | | -``` |
| 34 | +Currently, we support **Anthropic Claude Sonnet 4.0** as the AI model. To get started: |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +1. **Set up your environment:** |
| 37 | + ```bash |
| 38 | + export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY='your-api-key-here' |
| 39 | + ``` |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +2. **Install Jupyter AI Agents:** |
| 42 | + ```bash |
| 43 | + pip install jupyter_ai_agents |
| 44 | + pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt |
| 45 | + pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17 |
| 46 | + ``` |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +3. **Launch JupyterLab with the required configuration:** |
| 49 | + ```bash |
| 50 | + jupyter lab |
| 51 | + ``` |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | +4. **Access the chat interface** through the right panel in JupyterLab. |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +### What's Coming Next |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +We're actively working on expanding the capabilities of Jupyter AI Agents: |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +- 🚀 **More LLM Providers**: Integration with additional AI model providers |
| 60 | +- ⚙️ **MCP Configuration**: Enhanced MCP server configuration options |
| 61 | +- 🔧 **Extended Tool Access**: Chat access to tools from other MCP servers |
| 62 | +- 🛠️ **Enhanced Features**: And much more! |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | +Check out our [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-ai-agents/issues) to see what we're working on. **Contributions are welcome!** |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | +> **Note**: The documentation at https://jupyter-ai-agents.datalayer.tech will be updated soon to reflect the new chat features and capabilities. |
37 | 67 |
|
38 | | -This library is documented on https://jupyter-ai-agents.datalayer.tech. |
39 | 68 |
|
40 | | -## Install |
| 69 | +<details> |
| 70 | +<summary><strong>🖥️ CLI Usage</strong></summary> |
41 | 71 |
|
42 | | -To install Jupyter AI Agents, run the following command. |
| 72 | +## CLI Usage |
| 73 | + |
| 74 | +You can also use Jupyter AI Agents through the command line interface for automated notebook operations. |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | + |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | +### Basic Installation |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | +To install Jupyter AI Agents, run the following command: |
43 | 82 |
|
44 | 83 | ```bash |
45 | 84 | pip install jupyter_ai_agents |
46 | 85 | pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt |
47 | 86 | pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17 |
48 | 87 | ``` |
49 | 88 |
|
50 | | -Or clone this repository and install it from source. |
| 89 | +Or clone this repository and install it from source: |
51 | 90 |
|
52 | 91 | ```bash |
53 | 92 | git clone https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-ai-agents |
54 | 93 | cd jupyter-ai-agents |
55 | 94 | pip install -e . |
56 | 95 | ``` |
57 | 96 |
|
58 | | -The Jupyter AI Agents can directly interact with JupyterLab. The modifications made by the Jupyter AI Agents can be seen in real-time thanks to [Jupyter Real Time Collaboration](https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user/rtc.html). Make sure you have JupyterLab installed with the Collaboration extension. |
| 97 | +### JupyterLab Setup |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +The Jupyter AI Agents can directly interact with JupyterLab. The modifications made by the Jupyter AI Agents can be seen in real-time thanks to [Jupyter Real Time Collaboration](https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user/rtc.html). Make sure you have JupyterLab installed with the Collaboration extension: |
59 | 100 |
|
60 | 101 | ```bash |
61 | 102 | pip install jupyterlab==4.4.1 jupyter-collaboration==4.0.2 |
62 | 103 | ``` |
63 | 104 |
|
64 | | -We ask you to take additional actions to overcome limitations and bugs of the pycrdt library. Ensure you create a new shell after running the following commands. |
| 105 | +We ask you to take additional actions to overcome limitations and bugs of the pycrdt library. Ensure you create a new shell after running the following commands: |
65 | 106 |
|
66 | 107 | ```bash |
67 | 108 | pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt |
68 | 109 | pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17 |
69 | 110 | ``` |
70 | | - |
71 | | -## Use from the CLI |
| 111 | +### Examples |
72 | 112 |
|
73 | 113 | We put here a quick example for a Out-Kernel Stateless Agent via CLI helping your JupyterLab session. |
74 | 114 |
|
@@ -124,21 +164,23 @@ jupyter-ai-agents explain-error \ |
124 | 164 |
|
125 | 165 | 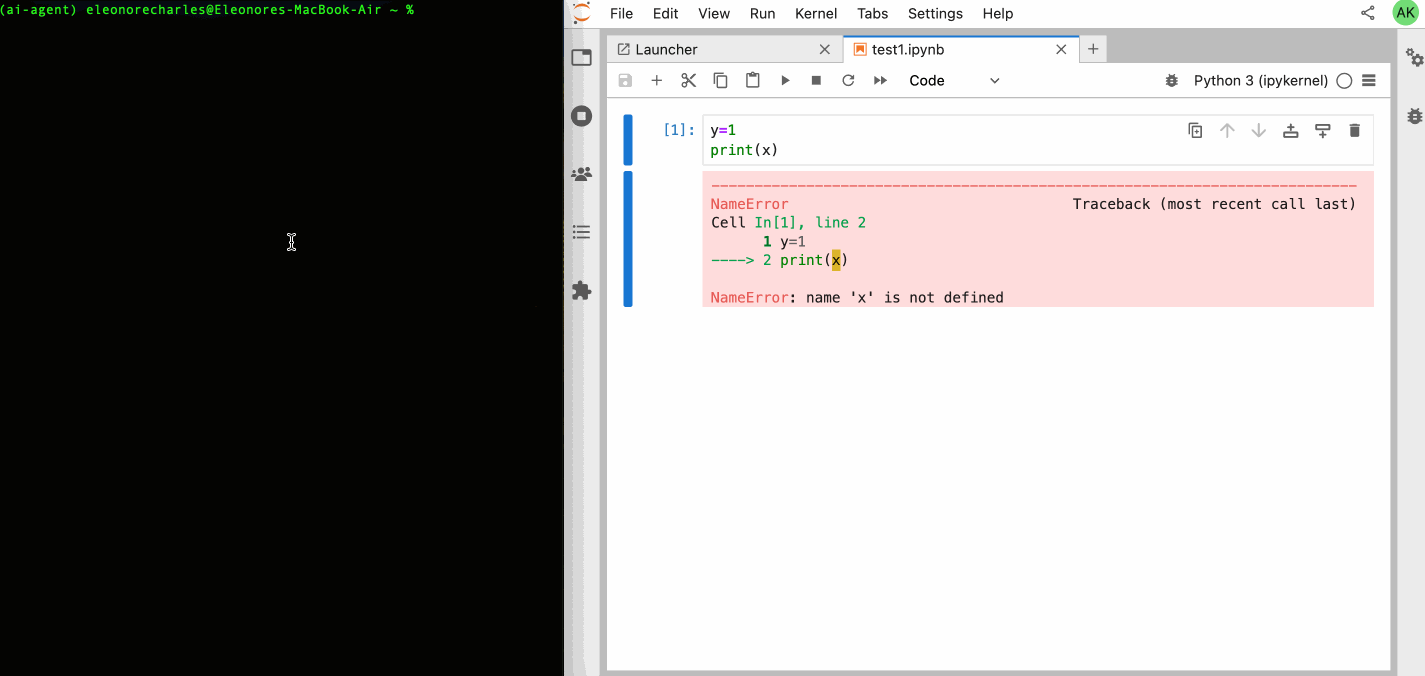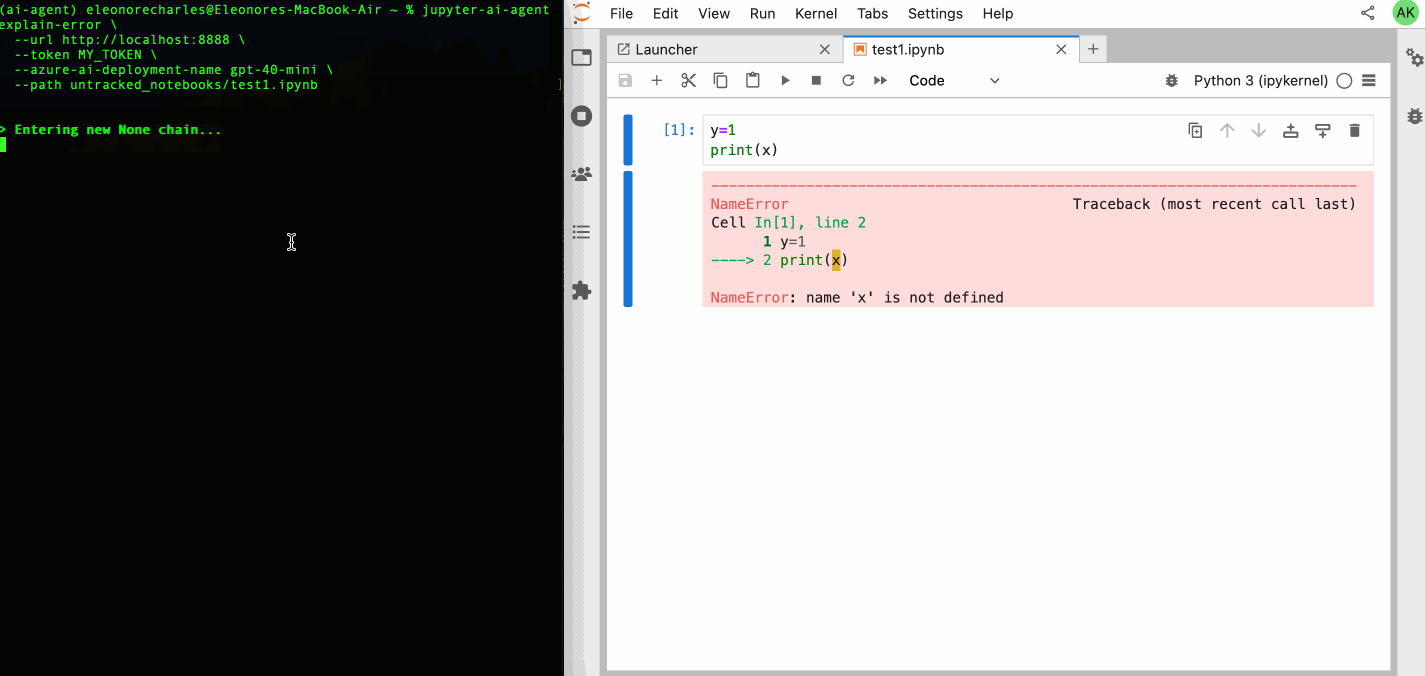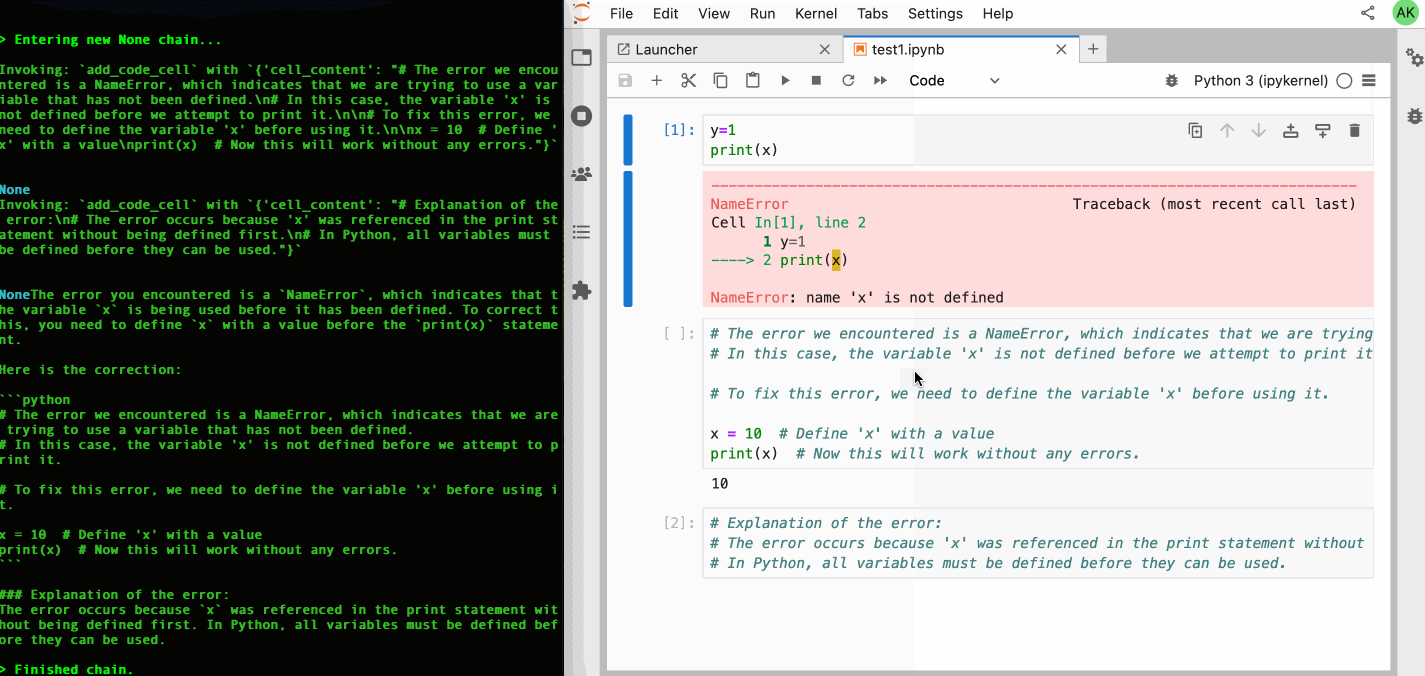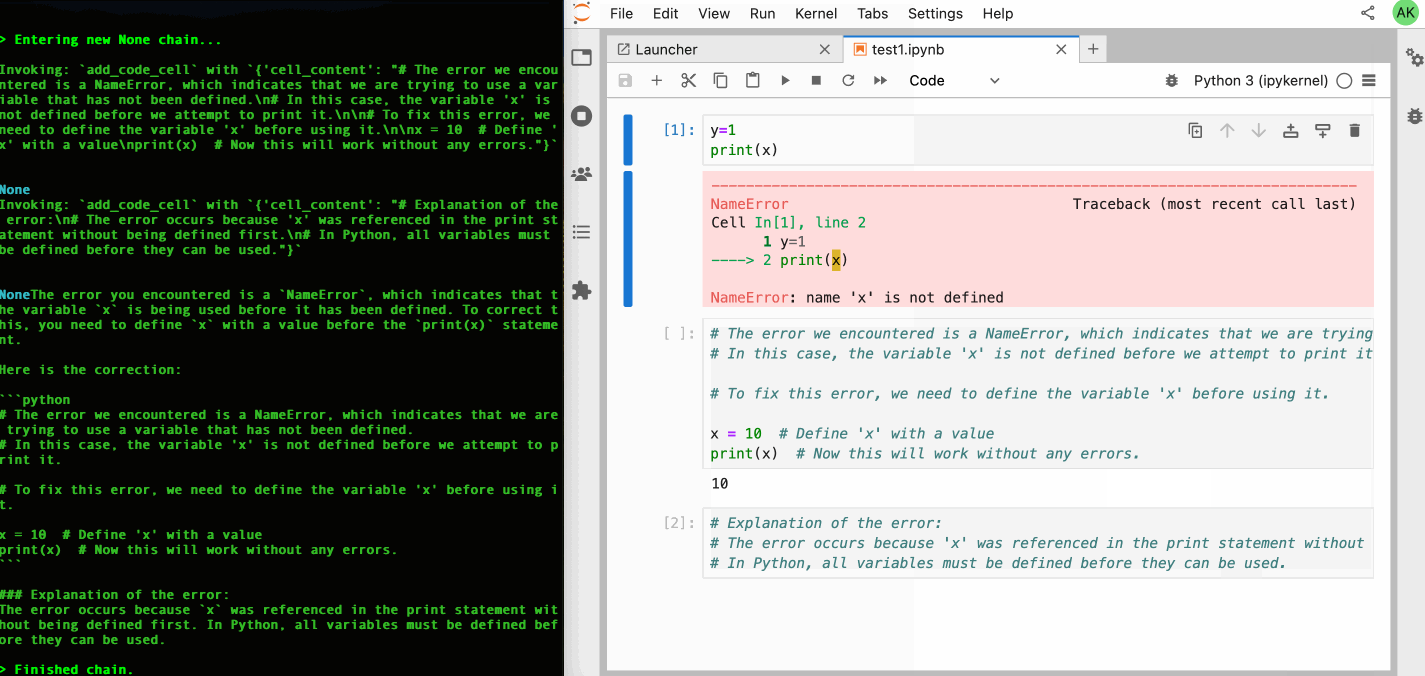 |
126 | 166 |
|
127 | | -## Uninstall |
128 | 167 |
|
129 | | -To uninstall the agent, execute. |
| 168 | +### About the Technology |
130 | 169 |
|
131 | | -```bash |
132 | | -pip uninstall jupyter_ai_agents |
133 | | -``` |
| 170 | +Jupyter AI Agents empowers **AI** models to **interact** with and **modify Jupyter Notebooks**. The agent is equipped with tools such as adding code cells, inserting markdown cells, executing code, enabling it to modify the notebook comprehensively based on user instructions or by reacting to the Jupyter notebook events. |
134 | 171 |
|
135 | | -## Deploy in a Server |
| 172 | +This Agent is **innovative** as it is designed to **operate on the entire Notebook**, not just at the cell level, enabling more comprehensive and seamless modifications. |
136 | 173 |
|
137 | | -You can start a Jupyter AI Agents server to be used in combination with the [Datalayer online services](https://datalayer.app). |
| 174 | +The Agent can also run separately from the Jupyter server as the communication is achieved through RTC via the [Jupyter NbModel Client](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-nbmodel-client) and the [Jupyter Kernel Client](https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-kernel-client). |
138 | 175 |
|
139 | | -```bash |
140 | | -make server |
141 | 176 | ``` |
| 177 | +Jupyter AI Agents <---> JupyterLab |
| 178 | + | |
| 179 | + | RTC (Real Time Collaboration) |
| 180 | + | |
| 181 | +Jupyter Clients |
| 182 | +``` |
| 183 | +</details> |
142 | 184 |
|
143 | 185 | ## Contributing |
144 | 186 |
|
|
0 commit comments